Violence erupted on Thursday (29 April) on another border area in the former Soviet space, this time in Central Asia. A ceasefire now appears to be holding on the border area between Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan but both sides report casualties in yesterday's clashes.
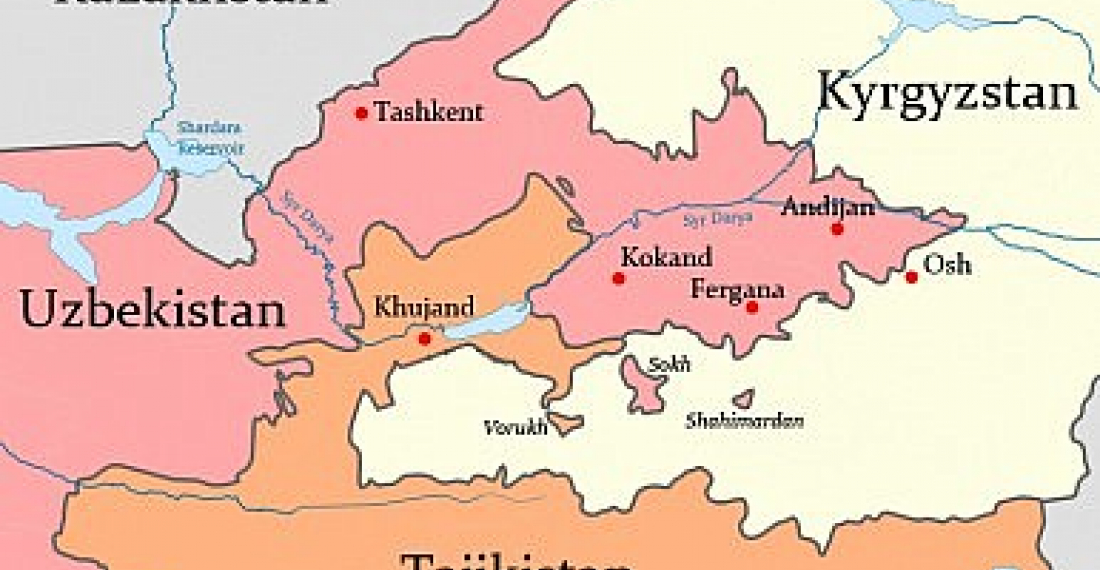
A conflict over a disputed water distribution facility on the border between Tajikistan and Kyrgyzstan, which broke out on the morning of April 29, quickly moved from stone throwing clashes between civilians to gunfights involving border guards and government forces, the Russian newspaper Vedomosti writes.
According to Stas Pritchin, an expert at the Russian Academy of Sciences' Institute of World Economy and International Relations, there are no external reasons for a violent conflict between the two Central Asian countries at the moment, but Tajikistan and Kyrgyzstan have had a long history of border disputes as both have enclaves on each other's territory. However, even when the authorities show some willpower to resolve border conflicts, local communities and criminal groups are not always willing to do the same, the expert added.
Expert on Central Asia Alexander Knyazev, in turn, told Nezavisimaya Gazeta that the border issue had long been neglected, particularly as far as Kyrgyzstan is concerned, because frequent changes of government forced the country to start solving its problems from scratch.
"On the whole, neither Kyrgyzstan nor Tajikistan is ready to address the border issues. Border regions in both countries are socially and economically depressed. The Fergana Valley lacks agricultural resources - land and especially water. This is why land and water have become the main cause of all conflicts," the expert noted.
"Since the collapse of the Soviet Union, aggressive nationalist sentiment has been increasing among locals both in Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan. The young generation was brought up in an atmosphere of aggression against their neighbors. That’s why even if the parties try to employ civilized methods to solve the problem, it won’t work in the foreseeable future. Long and painstaking work needs to be done," Knyazev pointed out.