Iran continues to closely follow the peacekeeping and humanitarian mission in Nagorno Karabakh. Foreign Minister Javad Zarif will be visiting Baku and Moscow this week to discuss the situation in Karabakh. Iranian border security will be a key issue according to officials.
Last Wednesday, Hesamodin Ashena, the senior advisor to Iran's President held separate meetings with ambassadors of Azerbaijan and Armenia in Tehran.
Hesamodin Ashena (@hesamodin1), the senior advisor to #Iran's President and the head of the Center for Strategic Studies (CSS) held separate meetings with ambassadors of #Azerbaijan and #Armenia in Tehran on Wed. pic.twitter.com/v7wVWDLkTK
— MAYSAM BIZÆR میثم بیزر (@m_bizar) November 19, 2020
Iran officially welcomes the end of hostilities. The agreement is largely in line with the Iranian plan proposed last month. The Spokesperson of the Russian Foreign Ministry said that Russia would address the issue of foreign fighters in the region which was one of Iran’s main concerns. Another positive aspect for Iran, highlighted by Parsine News, is that several cities near the border with Iran need to be rebuilt. This could encourage trade with Iran in the short term.
However, not everyone in Iran is optimistic about the Russian deal. One of the most significant changes in the new Nagorno Karabakh agreement is the Azerbaijani control of the border with Iran. Several analysts have said that the situation could pose future tensions as nearly the entire border region south of the Aras river is inhabited by ethnic Azerbaijanis. There are legitimate fears that a separatist movement could threaten future relations between Azerbaijan and Iran. Besides ethnicity, the ninth clause of the agreement is a concern for Iranian scholars and political analysts. The clause stipulates the following:
The Republic of Armenia guarantees the safety of transport links between the western regions of the Republic of Azerbaijan and the Nakhichevan Autonomous Republic in order to organize the unimpeded movement of citizens, vehicles and goods in both directions.
Ehsan Movahedian, a university lecturer and international relations researcher discussed the potential “economic consequences” of the agreement with Fars News Agency. Movahedian says Turkey and Azerbaijan will no longer need Iran to access the Nakhichevan region thus reducing its dependency and possibly causing financial losses to Iran. Until now, land connections between Azerbaijan and its Nakhichevan exclave passed through Iranian territory. On the other hand, Russian Middle East expert Mayis Gurbanov says that due to the Nakhchivan corridor, Iran will be able to compete more with the European Union because the cost of supplying goods will be reduced by using this plan.
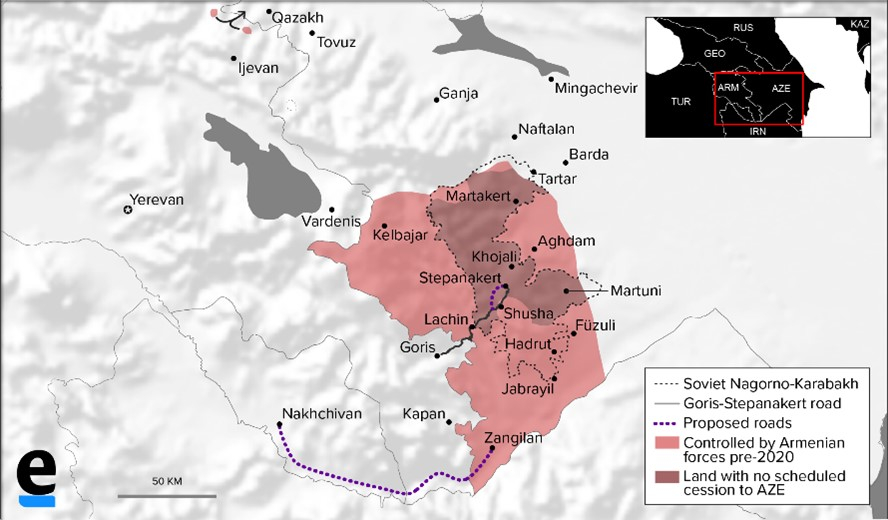
Abbas Araghchi, Deputy Foreign Minister of Iran, dismissed the concerns. He also dismissed online rumors that a geographical strip will be created between Iran and Armenia.
There will be no change in Iran's transit routes to Armenia or Azerbaijan.
Araghchi described the proposed Nakhichevan corridor as a transit route and not a substitute for roads that pass across Iran.







