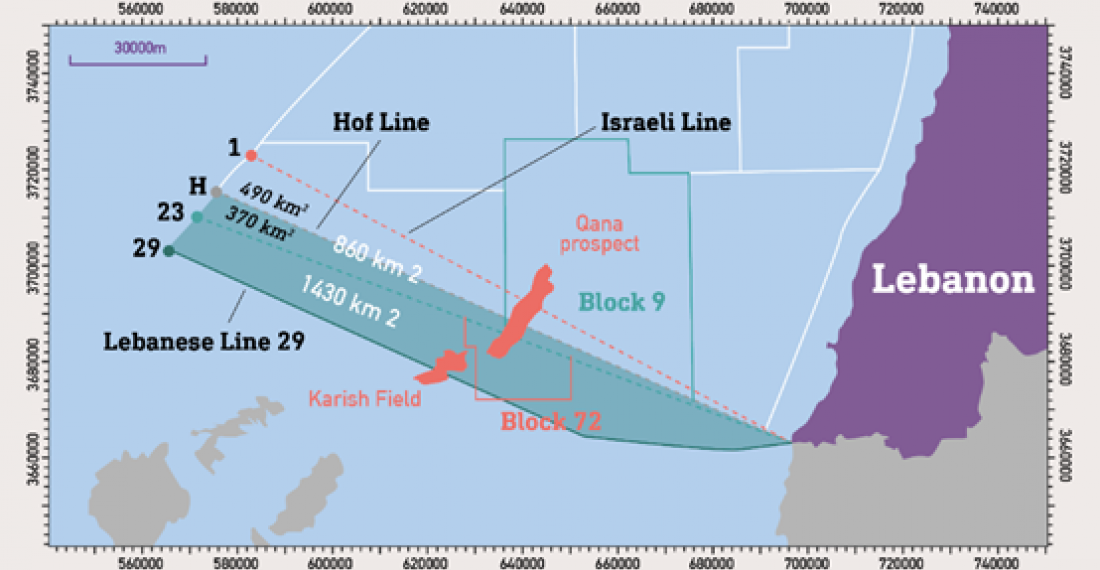
For years, Lebanon and Israel have been embroiled in a territorial dispute centred around two major natural gas fields in the Levantine basin, lying off the coast of their common land border. Qana is the Northernmost field, while the Karish field lies just to the South. The issue is of particular importance given that a 2010 US Geological Survey estimated that the Levantine basin could hold as much as 1.7 billion barrels of recoverable oil and 34.5 trillion cubic metres of gas. Lebanon and Israel have been feuding for more than a decade over their respective maritime claims. In 2010, Lebanon submitted a claim to the UN fixing their claim on what came to be known as Line 23 which would limit Israel to the entity of the Karish field, as well as the Southernmost part of Qana. Using a different calculation method, Israel pushed for Line 1, which would give it all of Karish and most of Qana. Talks were held in 2012, during which a midway solution was proposed by US mediators (Line H), but this compromise was turned down by Lebanon.
Then, in 2020, Lebanon amended its claim using new studies, arguing that the proposed border should be even further South, at Line 29. The new proposal, which would have given Lebanon all of Qana as well as almost all of Karish, was considered unacceptable by both Israel and the US. Talks were held in 2020 to try and reach an understanding, but the negotiations once again broke down, with both sides refusing to budge.
The situation seemed to have reached an impasse and stalled, until an Israeli-contracted vessel arrived at the Karish field earlier this month and began drilling just South of Line 29. Lebanese authorities responded with indignation, calling for a halt to drilling until the dispute had been resolved, and the border drawn. The situation was then further complicated by Hezbollah, who threatened to strike the rig if production began before an agreement had been reached.
Because Lebanon and Israel are officially still at war, and have no diplomatic relations between them, Beirut hastily invited Amos Hochstein, the US Senior Advisor for Energy Security, to mediate indirect talks and attempt to resolve the issue. After his meetings in Lebanon last week, it seemed that a breakthrough had finally been reached, when the Lebanese president, Michel Aoun, reportedly presented a unified position on behalf of the government, which saw it drop mentions of Line 29, as well as any claim to the Karish gas field. This new proposal would create an S shaped maritime border, granting Lebanon access to the whole of the Qana field, while leaving Israel the entirety of Karish. In the past, the lack of agreement within the Lebanese government over whether to push for Line 23 or 29, and its unwillingness to compromise had been the key factors holding back negotiations, and this new approach led Hochstein to strike an optimistic note, saying that Lebanon had taken “a very strong step forward”. The US Energy advisor will now relay the offer to Israel and await a response. Both countries stand to gain from a swift and peaceful resolution to this decade long problem which has prevented them from extracting any value out of the fields.
Lebanon in particular would benefit from the potential financial gains, given the current state of its economy and the inability of the government to provide even the most basic of necessities to most of its citizens. The Lebanese lira has reached an all-time low against the dollar, and as the economic crisis worsens, more and more Lebanese people are pushed into poverty. Food, water, and energy shortages are acute and chronic - a UN report earlier this month warned that nearly 80% of households did not have food or the financial resources to purchase food. Corruption and factionalism remain rampant, and Hezbollah’s influence continues to weigh over Lebanon. The causes of Lebanon’s problems are deep-seated, and solutions will not be found overnight.
The development of Qana is by no means a silver bullet, and it will take time for the benefits of any gas discoveries to filter through to ordinary Lebanese people. The French oil energy company Total, part of the energy consortium which signed a deal with Lebanon, refused to continue exploration until the issue was settled. Resolving the current dispute would allow Lebanon to start exploring the Qana field, and might allow for the production of cheap, domestically-produced energy, bolstering government coffers and providing an important step towards addressing the ongoing energy crisis.
Aside from the obvious economic benefits which will come from developing the Karish field, increasing its production of gas is also in Israel’s political interest. It has ambitions to become a major energy player, both regionally and globally, as exemplified by the recent landmark deal which will see it send billions of dollars’ worth of natural gas via Egypt to the European Union. As well as Cairo, Israel also has an agreement with Jordan to export energy. It will be hoping that gas diplomacy and increasing energy interdependence can help contribute to the ongoing thawing of relations with some of its Arab neighbours.
source: Anton Macfadyen is a research associate at LINKS Europe
photo: Map showing various claims by Lebanon and Israel regarding their maritime border
The views expressed in opinion pieces and commentaries do not necessarily reflect the position of commonspace.eu or its partners