Trending
EU and US make a generous financial pledge to Armenia as they affirm their support for its sovereignty, democracy, territorial integrity, and socio-economic resilience
5 April 2024
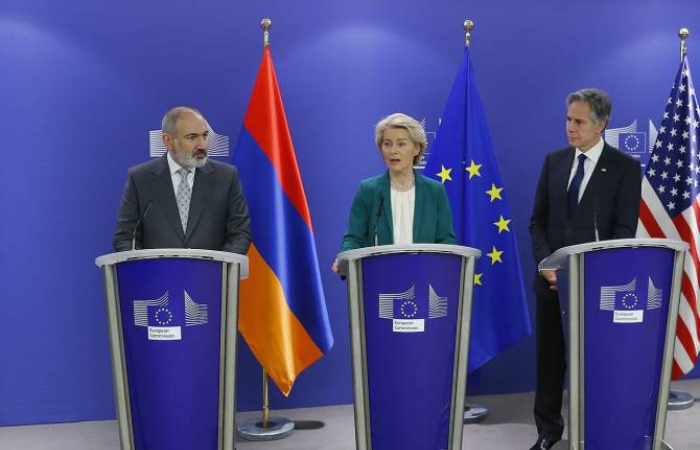
The European Union and the United States have made a generous financial pledge to Armenia and reaffirmed their support for its sovereignty, democracy, territorial integrity, and socio-economic resilience.
President of the European Commission, Ursula von der Leyen, EU High Representative/Vice-President, Josep Borrell, Secretary of State of the United States of America, Antony Blinken, USAID Administrator Samantha Power, and Prime Minister of the Republic of Armenia, Nikol Pashinyan, met today, April 5, 2024 in Brussels to reaffirm support for Armenia's sovereignty, democracy, territorial integrity, and socio-economic resilience. The statement concluded by saying that "A prosperous, sovereign, and democratic Armenia that develops its own partnerships and freely sets its own course will contribute to regional stability and prosperity."